“An effective way to increase supply-chain resilience is to understand the impact a crisis could have, well before it happens.” – McKinsey
Supply chain disruptions are caused by many different kinds of global events, like:
- Natural disasters
- Cross-country trade conflicts
- Military tensions across country borders
- Domestic crises
- Global epidemics and pandemics
- Recessions and other global crises
Now, what’s the impact of these disruptions on supply chains and the economy?
Examples of supply chain disruptions and their impact on the global economy
- Natural disasters: The massive earthquake and tsunami that affected Japan in 2011 resulted in $210 billion in costs for Japan. Due to supply chain disruptions, motor industry giants like Toyota, Nissan, and G.M. couldn’t ship or receive parts. This resulted in a temporary shutdown of their facilities across the globe. In situations like these, strategies like lean manufacturing don’t work either.
- Cross-country trade conflicts: South Korea is the world’s second-largest semiconductor manufacturer. (Semiconductors or related equipment account for one-third of Korea’s exports.) In 2018, South Korea exported $8.4 billion worth of semiconductors each month. However, the raw material to make these semiconductor materials came from Japan – which imposed export restrictions on these chemicals. This dramatically impacted South Korea’s economy and impacted global markets that depended on South Korea’s semiconductor production.
- Military tensions across country borders: India is an upcoming global economy. The Kargil war that took place in 1999 cost India $1 billion per week. That’s a lot of money. And for a developing country like India, a war can raise its fiscal deficit by 50%, directly impacting global trade. Not to forget, Pakistan is a much smaller country with a higher fiscal deficit and international debt. This caused a direct disruption in supply chain movements between the two countries during the war.
- Regional crisis: Brexit is reported to affect the efficiency and cost-effectiveness of global supply chains. Custom duties, extra tariffs, possible penalties, and other trade barriers can significantly slow down pan-European business, costing billions of dollars to both manufacturers and governments.
- Epidemics & Pandemics: In a report released by FAS, it’s been estimated that global trade fell by 5.3% in 2020. In March 2020, the World Health Organization declared the emergency a pandemic, resulting in an economic crisis that negatively affected the $90 trillion global economies.
- Global Crises: Forbes called the 2016 Oil Crisis “The Worst Oil Crash In A Generation.” Crude oil prices fell as low as $20 a barrel. Sometimes, it fell to $10 too. The World Bank says a growing supply surplus drove the collapse in oil prices. Whatever the cause was, the consequences were brutal. No new energy investment projects were made during this period. The Middle East to Central America, whose economies are entirely reliant on oil exports—were on the brink of an economic collapse due to this oil crash crisis.
The above are the major causes of broken supply chains.
How to adapt to supply chain emergencies and build resilient supply chain systems
By answering these critical questions:
- Does your supply chain system have a risk identification and mitigation strategy in place?
- Do you know how to leverage your supply chain resilience using digital tech?
- How do you transform a humongous, rigid supply chain into a flexible, agile operational model?
Customers today naturally expect their favorite brands to anticipate their needs instead of waiting for events to unfold.
That’s how much the supersonic eCommerce industry has changed the way supply chains work today.
So how do we build resilient supply chains that are also agile and flexible?
3 ways to improve supply chain robustness
|
|
|
Holistic overview and end-to-end visibility in supply chains
To operate a supply chain smoothly, many activities, events, KPIs, and metrics need monitoring, tracking, and optimizing.
A rigorous supply chain functions by keeping track of the warehouses’ incoming, outgoing, and idle inventory.
Without this information, there’s no way to track if deliveries are happening as they should be.
On a granular level, to make data-informed business decisions, some of the basic parameters to track are: spend summary, charges summary, service overview, parcel charges, weekly savings from parcel charges, optimizing shipment, distribution center tracking, and overview, the volume of packages shipped, etc.
These parameters indicate the state of your supply chain operations.
For continuous growth, resource allocation, and improvement of your supply chain operations, it’s important to have instant, accurate, real-time access to operational information. Having access to this data helps improve functional efficiencies, optimize manufacturing routines and save costs.
Real-time responsiveness to internal and external stimuli
SCMResearch defines supply chain robustness as the ability of a supply chain to resist or avoid change/ the unknown.
With accurate data and a detailed, on-demand supply chain overview in hand, you’ve already covered the two major steps in disaster management.
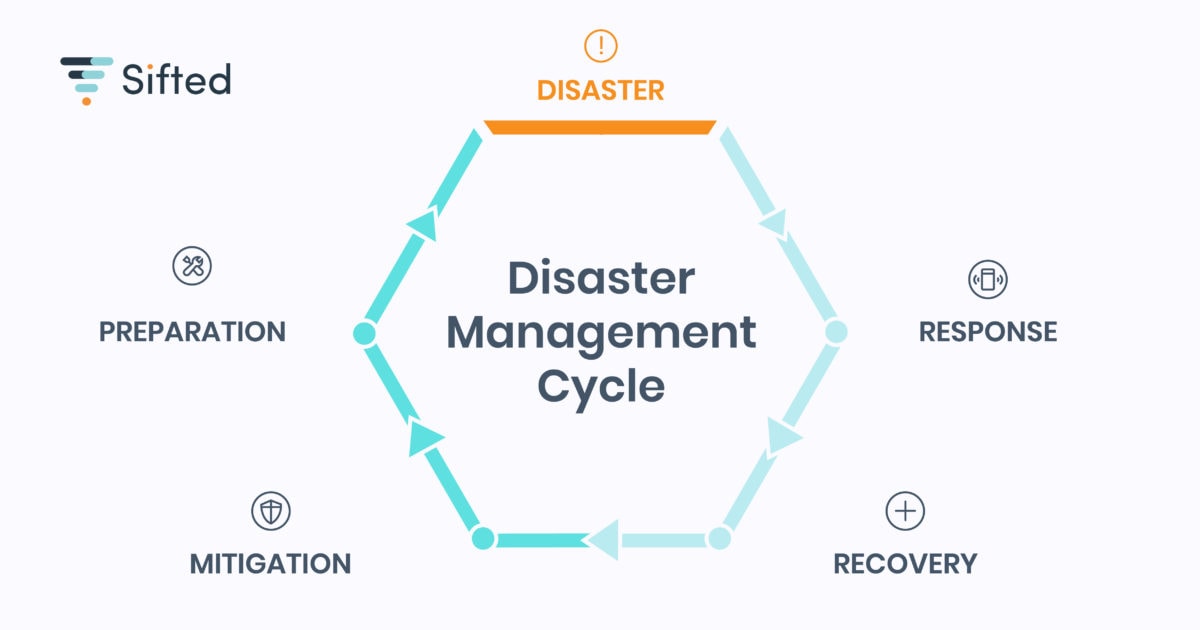
The above image represents 4 phases of the disaster management cycle.
- Preparedness
- Mitigation
- Responsiveness
- Recovery
In case of an emergency, you don’t need to design a crisis map from scratch when you have quantitative analytics at your disposal.
For example, let’s say there’s a freight cargo emergency. Let’s assume one of the cargo flights carrying your priority shipments is delayed and is stranded in one of the transit airports due to bad weather.
Instead of panicking and contacting the 3PLs responsible for pickup and delivery, what you could do is sit down with your data.
Trace back the customer details using the package shipment info and alert the affected customers by communicating the crisis beforehand, instead of waiting until the last minute and disappointing your customers.
A simple email or message informing the customer about the crisis does a lot more good than no communication at all.
With this step, you’ve checked off:
- Preparedness – within minutes, you could resolve customer-level crises by accessing data.
- Risk Mitigation – You saved the brand hundreds of angry, disappointed, negative reviews. This means you’ve retained these customers successfully.
Now that the above steps are taken care of, you can think about what to do to get the packages to safety and delivered ASAP without worrying about your customers’ glorious wrath at you.
Adopting logistics intelligence to track, manage, and optimize supply chains
None of the above risk management strategies would be possible without a powerful, accurate, robust logistics intelligence system.
A logistics intelligence system helps you tap into your supply chain’s mind and control its matter. Take proactive steps to optimize your supply chain operations by using real-time tracking status and a complete overview of your business that saves you money. Request a free demo here.











