Great news, your customer’s package arrived!
But something isn’t quite right. The box is melting, and it smells terrible.
Their food prep box was delivered, but it didn’t stay at the right temperature during transit. Now, the customer’s food is spoiled, and your money is wasted.
This is the reality of temperature-controlled shipping gone wrong, and it’s more common than you’d think.
So what is a cold chain?
A cold chain, or temperature-controlled supply chain, is the transportation of temperature-sensitive goods and materials.
Cold chain logistics impacts the supply chain by using technology and processes to maintain the refrigeration line from production to delivery. As a result, products are held at specific temperatures, or ranges, throughout their entire life cycle. Leaving no room for error within this cold supply line, as any divergence from required temperatures is catastrophic for the product’s delivery condition.
Due to the sensitivity of these parcels, interruptions in the supply chain could be dire. Unavoidable accidents/mistakes, whether natural or human-caused, could result in temperature drops or spikes- spelling disaster for shippers and their customers expecting a quality product.
Without the proper packaging, transportation equipment, precise timing, and carefully crafted routes, temperature-sensitive parcels don’t stand a chance for survival. So for companies and manufacturers that rely on their products’ temperatures being maintained throughout the supply chain, they must pay close attention to these crucial survival elements.
With such demanding guidelines, success can only be accomplished through data checkpoints throughout the cold chain, with teams who possess the knowledge and training for managing complex supply chain needs.
It’s a significant shipping hurdle that requires intricate choreography and lots of data to navigate through.
Why is cold chain logistics necessary?
Consumers are rarely aware of the backstage actions that occur when you order a product, online or in-store. For example, we purchase medications, food, and beverages from businesses and shops, with no second thought about how they arrived there. Or we enjoy a steak dinner at a local restaurant, unaware of how the meat was delivered – but we do expect a quality product.
At the same time, the “Amazon Effect” has resulted in overwhelming growth of consumer demand for the speedy delivery (two-day, one-day, same-day) of quality, fresh goods.
Consumers want their product in tip-top condition quickly.
Supply chain care
Suppliers, manufacturers, and carriers are catching on to the critical nature of maintaining temperature-sensitive goods. They understand the consequences of a broken cold chain and cannot afford gaps or fluctuations.
In addition, there are safety risks with these complex deliveries that could result in an inferior product and possible sickness to the end-user. For example, food products are associated with foodborne illness when not kept at an adequate temperature. – Let’s go back to the food prep box for further illustration.
While the food in the customer’s prep box was delivered in seemingly good condition, if the box spent a few hours in transit 5/10 degrees over or under their set temperature, the customer is now at risk. The product has now been compromised due to a lack of cold chain maintenance.
These risks only double when it comes to medications and pharmaceutical goods, which the Covid-19 pandemic further highlighted through the transportation of temperature-sensitive vaccines. To ship these vaccines safely, cold chain logistics must monitor each step of the supply chain link with data tracking technology to ensure their viability for end-use.
For example, the complex regulations in place for the transportation of the Covid-19 vaccines, Pfizer and Moderna, vary between the two and must be strictly adhered to. Any break in protocol will result in the loss of the vaccines due to spoiled ingredients that must be secured at set temperatures. Loss of vaccines means loss of resources, money, time, and possible lives. Once the vaccine has been compromised, it must be thrown out.
The stakes are high and dangerous for manufacturers whose products’ livelihood depends on a perfect cold chain.
How does cold chain logistics work?
Cold chain logistics involves preparing, storing, transporting, and monitoring the products through various elements. Manufacturers rely heavily on cold chain logistics to ensure their products are uncompromised and undamaged throughout the process.
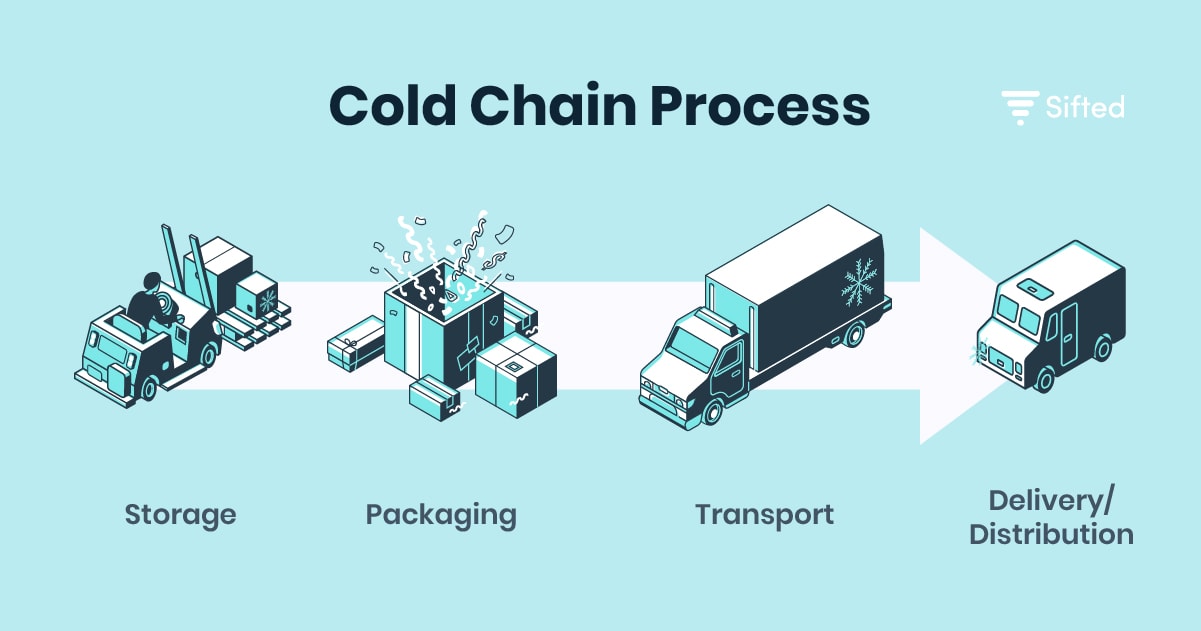
- Storage – Once the product leaves the manufacturer, the cold chain link begins. Products are kept in a specialized facility waiting to be transported and are maintained at set temperatures. These come in the form of blast freezers, refrigerated containers, chillers, cold boxes, and cold rooms.
- Packaging – An essential step to a successful cold chain is selecting the appropriate packaging for the product. Various options are available, from ice bricks and insulated mailers to flexible box liners, shipping coolers, and insulated packing systems. The packing type is dependent on the goods being transported.
- Transport – Using cold chain technology, refrigerated transportation can maintain stable temperatures during transit to avoid spoilage. Cold chain technology provides ways to hold the needed temperatures of the product safely. Various types of technology can be used depending on specific factors such as product size, transit time, vehicle capacity, and environmental influences.
-
-
- Dry ice – Useful for longer durations of travel to keep temperatures stable for extended periods.
- Reefers – A vehicle/van/truck that is temperature-controlled, with air circulation.
- Gel Packs/Bottles – Mainly used for food and pharmaceutical products to maintain cold or warm temperatures.
- Cold Plates – Similar to gel packs, but can be reused to refrigerate an area.
- Liquid Nitrogen – Intense cooling technology for advanced temperature control needs, like frozen products.
- Quilts – An insulated blanket/cover that can be wrapped around products to maintain temperatures.
- Carry Paks – Thermal container systems for the temperature preservation of products.
-
- Delivery/Distribution – Cold chain management is used to ensure that the time and temperature-sensitive package is delivered per the customer’s specifications.
These elements are all tracked with data logging and cold chain monitoring for complete transparency of the supply chain. This empowers shippers to implement changes in their cold chain processes for better performance moving forward.
———–
Without the technology to constantly maintain the temperatures and processes in your cold chain, you could be facing severe consequences.
- Ruined Product – Sensitive items are quick to spoil or lose their integrity. In addition, any slight deviation in temperature could cause the product to become useless.
- Wasted Money – Who is footing the bill when products go bad during transportation? The shippers. They lose the money they invested in the product and procure extra inventory to replace the spoiled goods.
- Tainted Reputation – Not only does brand reliability go down with a poor customer experience, but business partnerships also suffer. Partnerships can falter due to mistakes or losses during transportation.
With so many regulations and data points to keep track of, many manufacturers choose to collaborate with specialized cold chain logistics companies to meet their specific shipping needs. Through constant monitoring and data logistics, these manufacturers are provided a clear picture of what’s happening in their supply chain – Because empowered shippers make smarter choices.
Lack of protection and data are melting away the time and money you have invested in your products!
Do you need help monitoring your shipping along the cold chain?
Get more tips and tricks in our latest eBook, How to Eliminate Hidden Temperature-Controlled Shipping Costs.











